SeisSol
SeisSol is a high-performance computational seismology code designed to simulate complex earthquake scenarios and seismic wave propagation. Built upon the Arbitrary high-order DERivative Discontinuous Galerkin (ADER-DG) method, SeisSol enables precise modeling of earthquake source mechanisms, dynamic rupture processes, and resulting ground motion with unprecedented accuracy.
The code supports various material models including isotropic and anisotropic elastic, acoustic, viscoelastic, and poroelastic media, making it versatile for different geological conditions. SeisSol is particularly valuable for earthquake-tsunami coupled simulations, where acoustic coupling enables the modeling of tsunami generation and propagation following submarine earthquakes.
Designed for researchers in computational seismology, geophysics, and earthquake engineering, SeisSol serves earthquake simulation laboratories, early warning centers, and hazard assessment institutions worldwide. Its scalability on high-performance computing systems makes it an essential tool for large-scale seismic hazard studies and real-time earthquake analysis.
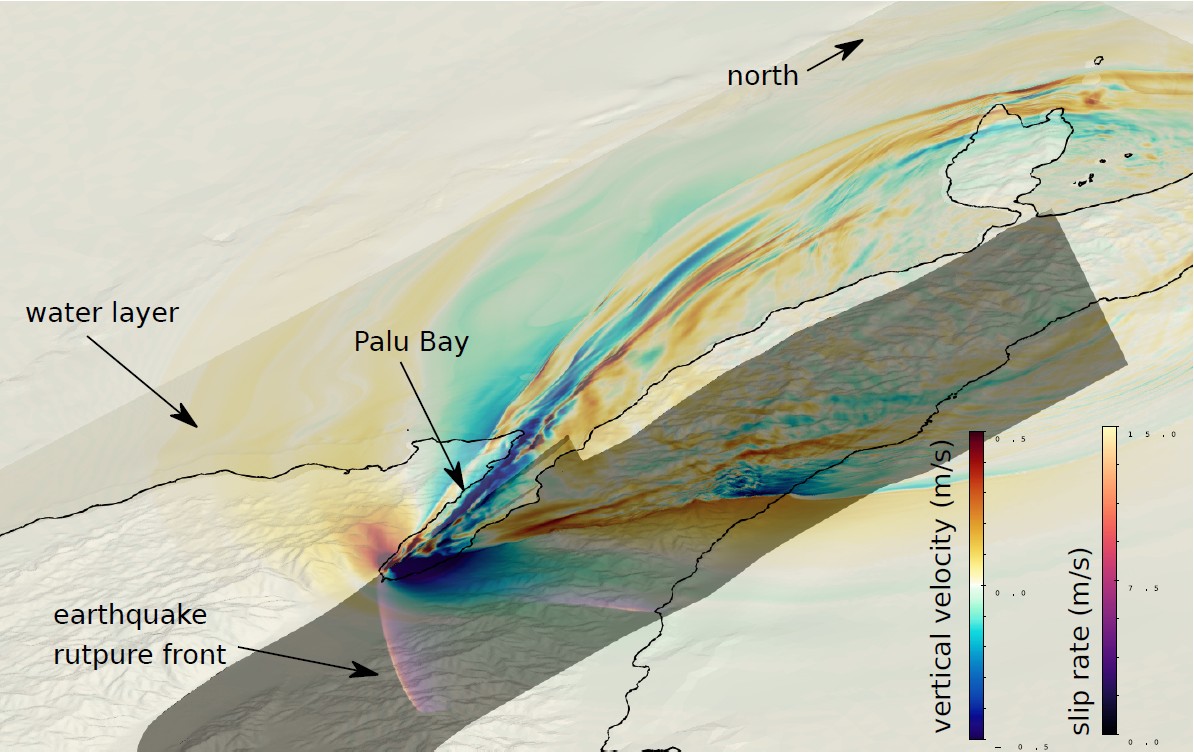
SeisSol enables dynamic rupture modelling on realistic geometries
Dynamic rupture simulation of the 2018 Palu (Sulawesi) earthquake and tsunami (Krenz et al., 2021); the respective SC21 paper also motivated the scenario for the Mystery Application for the SC22 Student Cluster Competition).
SeisSol in Scopus: Documents by year
No Data Found
By Subject
No Data Found
By Country
No Data Found
Analysis of the results from the bibliographic search on SeisSol. Scopus. (2025, July)
SeisSol In Video
SC23: Conversing Faults: The 2019 Ridgecrest Earthquake
Awards and Honors
- SC17 Best Paper Award, SC17 Supercomputing Conference, Denver, USA. Most prestigious prize for application driven high-performance computing awarding the longest and largest multi-physics simulations performed to date modelling the 2004 Sumatra-Andaman earthquake.
- IWSM 2017 Award Winning Poster. Bauer, Alexander, Fabian Scheipl, Helmut Küchenhoff, and Alice-Agnes Gabriel. (2017), Modeling spatio-temporal earthquake dynamics using generalized functional additive regression, in Proceedings of the 32nd International Workshop on Statistical Modelling, 3-7 July, 2017, Groningen, Netherlands.
- 2014 ACM Gordon Bell Prize Finalist, Association for Computing Machinery (ACM) at Supercomputing Conference SC14, New Orleans, USA. Highly competitive, annually awarded prize for outstanding achievements in high-performance computing. In our submission, we performed multi-physics simulations of a 1992 Landers earthquake scenario on the largest existing supercomputers.
- PRACE ISC Award 2014, best-paper-type prize awarded by the Partnership for Advanced Computing in Europe (PRACE) at the ISC High Performance conference. Our awarded paper featured the first petascale production run (wave propagation in Mount Merapi, with complex topography) with SeisSol on SuperMUC.
To Know More
Official Website
Acknowledgments
All copyrights belong to the seismology group @LMU and to the scientific computing group @TUM.