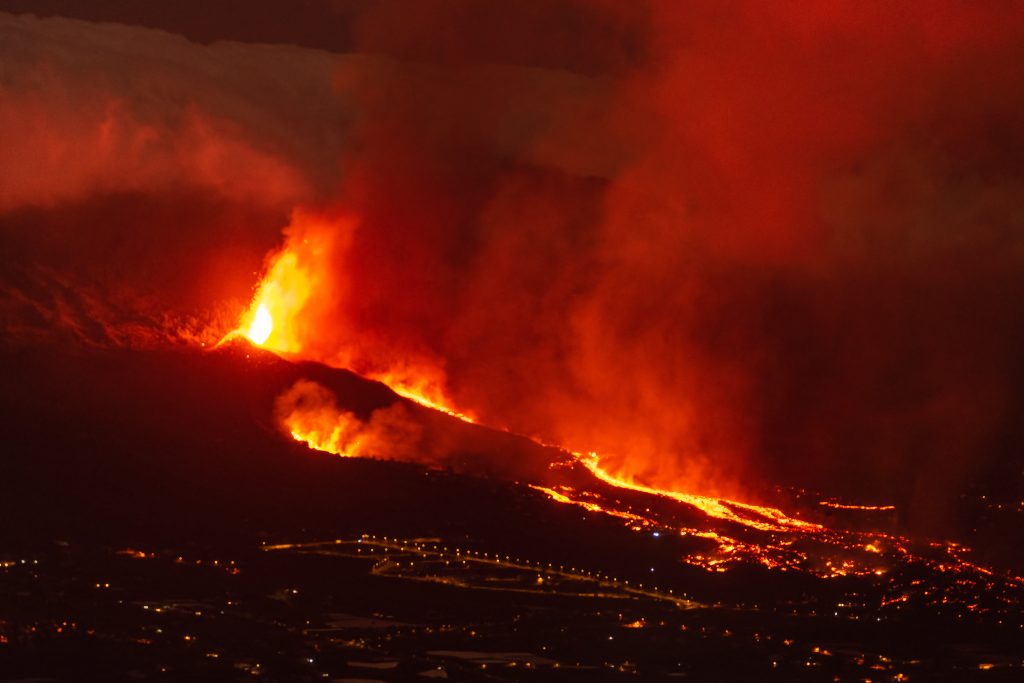
On September 19, 2021, the Cumbre Vieja volcano erupted on the Spanish island of La Palma, causing the destruction of 3,000 buildings and the evacuation of 8,000 people. Volcanic ash also intermittently disrupted air traffic to and from La Palma, presenting significant challenges for local authorities.
To shed light on how advanced computational tools can aid in such crises, Castiel organized the eighth webinar in their “Code of the Month” series, focusing on the essential codes used during the La Palma eruption: FALL3D and OpenPDAC. This webinar featured presentations by ChEESE researchers Arnau Folch and Mattia De’ Michieli Vitturi.
Held on Wednesday, May 29, the webinar highlighted how FALL3D and OpenPDAC support public authorities in making critical decisions during emergencies. FALL3D models the atmospheric consequences of volcanic eruptions, including the dispersal and sedimentation of particles and ashes. OpenPDAC simulates local-scale phenomena such as pyroclastic flows and ballistic ejecta associated with phreatic explosions, which are significant hazards evidenced by recent events at Ontake (Japan) and White Island (New Zealand). Within the ChEESE project, OpenPDAC will be used to assess the hazard from phreatic explosions at Vulcano Island (Italy).
The webinar underscored the capabilities of these codes, discussed ongoing and future developments, and addressed the challenges faced in their application. The audience, composed of attendees with varying levels of expertise and representatives from other Centres of Excellence, engaged actively, asking direct questions about the practical implementation of these tools.
This insightful session demonstrated the critical role of supercomputing in managing natural disasters and provided valuable knowledge to enhance emergency response strategies.
To know more about the codes: