LaMEM
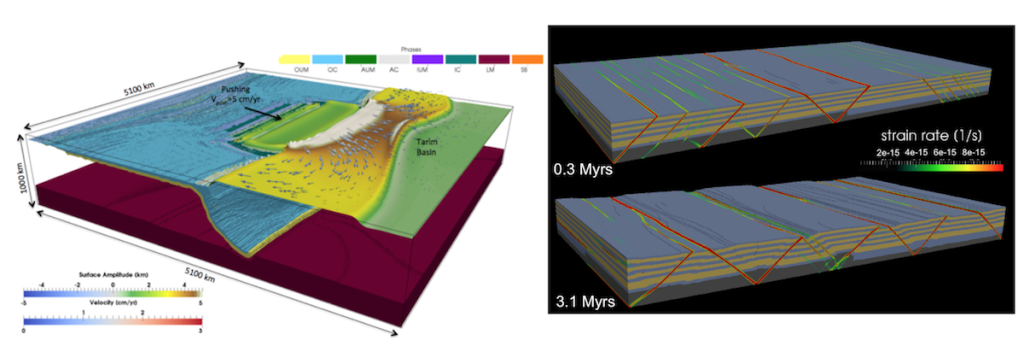
LaMEM (Lithosphere and Mantle Evolution Model) is an open-source 3D code used to study how the Earth’s lithosphere and mantle evolve over time. It helps researchers explore large-scale processes such as plate collisions, mountain building, rifting, and mantle flow. The code can represent different rock behaviors, from slow creeping flow to brittle failure, making it useful for both geodynamics and geomechanics.
To capture these complex processes, LaMEM combines a marker-in-cell approach with efficient numerical solvers. It can handle non-linear material properties, simulate gravity and fluid flow in porous rocks, and scale from small laptop tests to supercomputers with hundreds of thousands of processors.
This flexibility makes it suitable for both small experiments and large, high-resolution studies of Earth’s interior. LaMEM is widely used in the geoscience community and is part of collaborative projects such as ChEESE. Its strength lies in combining advanced physics with strong computational performance, giving a reliable tool to test ideas about how the Earth works deep below the surface.
Relevant Information
LaMEM in Scopus: Documents by year
No Data Found
By Subject
No Data Found
By Country
No Data Found
Significant publications
-
Kaus, Boris JP, et al. “Forward and inverse modelling of lithospheric deformation on geological timescales.” Proceedings of nic symposium. Vol. 48. John von Neumann Institute for Computing (NIC), NIC Series, 2016.
-
Popov, Anton, and Boris Kaus. “3D modelling of non-linear visco-elasto- plastic crustal and lithospheric processes using LaMEM.” EGU General Assembly Conference Abstracts. 2016.
-
Eichheimer, Philipp, et al. “Pore-scale permeability prediction for Newtonian and non-Newtonian fluids.” Solid Earth 10.5 (2019): 1717-1731.
-
Pusok, Adina E., Boris JP Kaus, and Anton A. Popov. “On the quality of velocity interpolation schemes for marker-in-cell method and staggered grids.” Pure and Applied Geophysics 174 (2017): 1071-1089.
-
Riel, Nicolas, et al. “Subduction initiation triggered the Caribbean large igneous province.” Nature Communications 14.1 (2023): 786.
To Know More
Developers
LaMEM is an open source code that was initially developed at the Johannes-Gutenberg University in Mainz (Germany). Many other colleagues have contributed to its development as well (see the documentation).
The key funding for the Mainz team came from:
The European Research Council through Grants ERC StG 258830 (MODEL), ERC PoC 713397 (SALTED) and ERC CoG 771143 (MAGMA)
The German ministry of Science and Eduction (BMBF) through projects SECURE, PERMEA, and PERMEA2.
Priority programs of the German research foundation (DFG), specifically the 4DMB and Habitable Earth projects.
License & Copyright
MIT License
Copyright (c) 2011-2023 JGU Mainz, Boris Kaus, Anton Popov
Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy of this software and associated documentation files (the “Software”), to deal in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:
The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in all copies or substantial portions of the Software.
THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED “AS IS”, WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM, OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE SOFTWARE.